Examples Of Homeostasis In The Human Body – Homeostasis is the tendency not to deviate from the range of favorable or ideal internal conditions. These conditions must remain constant. Maintaining a stable internal condition is crucial for any form of living being. Different physiological strategies are used to maintain the correct functioning of a system despite the dynamics of the external environment. In fact, this ability is one of the characteristics of being alive.
Instead of doing nothing, act and resist the effect of external factors so as not to deviate from the state of equilibrium, stability or balance that it favors. In humans, homeostasis is maintained by regulatory mechanisms, each of which consists of three general components:
Examples Of Homeostasis In The Human Body

. Therefore, as a feedback control system, the homeostatic process can be conceptualized as a closed-loop structure, meaning that the output of the system is fed back to the system as input, thus regulating future action. Positive feedback leads to greater stimulation or acceleration of the process, while negative feedback leads to inhibition of the (source of) stimulus or slowing down of the process.
Structure And Function Of The Human Body
Examples of positive feedback are labor contractions, blood clotting, and action potential generation. Examples of negative feedback systems are thermoregulation, blood glucose regulation, blood pressure baroreflex, calcium homeostasis, potassium homeostasis, and osmoregulation.
The definition of homeostasis in biology is the ability or tendency of the body or a cell to seek and maintain a condition of equilibrium.
– since these are external changes. It makes use of feedback controls and other regulatory mechanisms or dynamic processes to maintain a constant internal environment. It can be interpreted as an ability of a living organism in its effort to stay within the optimal range despite fluctuating environmental conditions. Thus, in the biological context, the word homeostasis implies multiple physiological control mechanisms to maintain and stabilize the functional and normal state of an organism.
, which means “standing”). The concept of homeostasis was first described in 1865 by Claude Bernard, a French physiologist. However, the term was later coined in 1962 by American physiologist Walter Bradford Cannon.
Homeostasis And Heat Regulation Poster
An organism needs a system that effectively interconnects various biological processes and functions. The human body, for example, has organs made up of cells that work in unison.
These organs, although different from each other, have to work together to maintain a set of internal conditions within the ideal range. There are various homeostatic processes and each of them works by regulating certain variables in the body’s internal environment.
The human body could not function efficiently if there is a prolonged imbalance in internal physical conditions and chemical composition. Like any other living being, the human body employs various homeostatic mechanisms to maintain optimal functioning.
Variables such as body temperature, pH, sodium level, potassium level, calcium level and blood sugar level must be maintained within the established limits.
Autism, Adhd, And Homeostasis
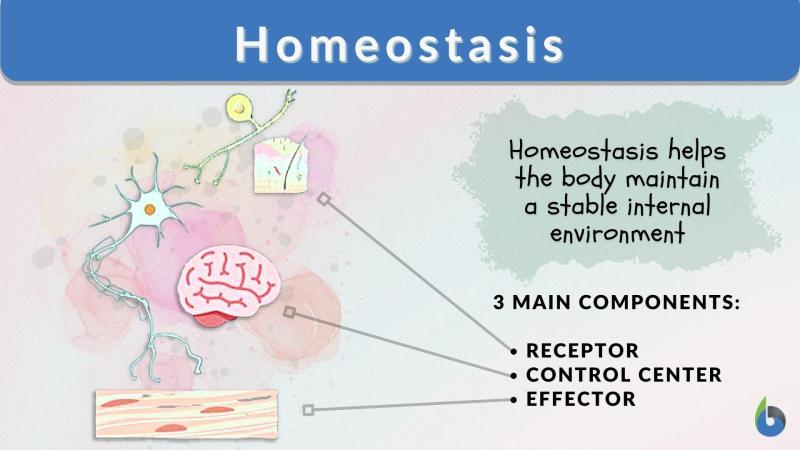
. The homeostatic range is defined as the upper and lower limits allowed for a particular variable. If the range of homeostatic values is exceeded, the body would soon stop performing its tasks and become dysfunctional. In order for the body to maintain these variables within effective limits, various regulatory mechanisms are used and each of them is composed of three general components.
Figure 1: The three main components of homeostasis are a receptor, a control center and an effector. The receiver collects information from its environment and transmits it to the control center. The control center, in turn, processes the information and sends signals to the effector. The effector then produces a response based on the signal from the control center.
Information about the condition of the corpse. Monitors and perceives changes in its environment, both internal and external. It is in the form of a sensory nerve terminal that receives information (i.e., stimulus) and then responds by producing a nerve impulse depending on the type, presence/absence, or degree of stimulation. Examples of receptors in the human body are the following:
They belong to the homeostatic component that processes the impulses transmitted by the receptors. Some examples are the respiratory center and the renin-angiotensin system.
Homeostatic Maintenance Of The Lymphatic Vasculature: Trends In Molecular Medicine
Are the target of the homeostatic response that would cause the reversion of conditions to the optimal state or
Range. At the tissue or organ level, they are exemplified by the muscle or gland. At the cellular level, they are the receptors on a nerve, including nuclear receptors.
These three components function by first detecting and then responding to information (i.e., stimulus) by sensory cell receptors. These cells respond to the change detected in the environment by transmitting the information to the control center to

In the control center involves deliberation and determination of the appropriate response to the transmitted stimuli. Then send this
What Is Homeostasis? » Science Abc
Would provoke the supposed response that would return to the normal homeostatic range. At the cellular level, activated nuclear receptors will act by upregulating (or downregulating) the expression of certain genes. The protein produced from gene expression would then exert its effect on the target organ.
Examples include labor contractions, blood clotting, and action potential generation. Negative feedback is a self-regulatory system and is used in several biological systems. He
The direction of the stimulus and tends to inhibit the source of the stimulus or slow down the metabolic process. Examples include thermoregulation, blood glucose regulation, blood pressure baroreflex, calcium homeostasis, potassium homeostasis, and osmoregulation.
Labor contraction during childbirth is a positive feedback as the initial contraction of the uterine muscle leads to more contractions. Instead of inhibiting contraction, the body tends to produce more contractions. During labor, the posterior pituitary gland releases oxytocin which stimulates muscle contraction. During childbirth, the release of oxytocin increases further, intensifying muscle contractions until the newborn is pushed out of the birth canal.
Solution: Homeostasis And Internal Environment Essay
The formation of a blood clot in the presence of tissue injury is an example of positive feedback. The conversion of blood from liquid to solid form involves a series of activations of clotting factors. As soon as one clotting factor is activated, the next clotting factor is activated, resulting in the formation of a fibrin clot. In this process the direction of the stimulus is maintained.
In neuronal signaling, positive feedback is demonstrated during membrane depolarization. As the nerve impulse is transmitted along the neuron’s axon, voltage-gated sodium channels open in series along the axon. The first set of voltage-gated sodium channels open, resulting in the influx of sodium ions. This, in turn, causes depolarization of the surrounding area, meaning the next set of voltage-gated sodium channels will open.
Homeostatic regulation of body temperature in the winter (left) and summer (right) seasons. In winter, thermoreceptors detect a drop in body temperature and transmit this information to the anterior hypothalamus and preoptic area of the brain. The brain centers then initiate homeostatic control mechanisms to return core body temperature to the normal level.

. In summer, the body corrects the increase in core temperature by dissipating heat and evaporative cooling mechanism through sweating. Image prepared by María Victoria Gonzaga for Biology Online
Homeostasis And The Nervous System — The Science Sauce
Thermoregulation is an example of negative feedback. It refers to the homeostatic regulation of body temperature. The human body tends to maintain an internal temperature of approximately 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit (98.6 ˚F, equivalent to 37 ˚C), also known as body temperature.
When the ambient temperature is lower than the skin temperature, heat loss occurs. This means that in colder environments (for example, during the cold winter season), the body loses heat mainly from the hands and feet. As a result, the core temperature drops. This is picked up by the thermoregulatory center of the brain as a
Internal environment and initiates control mechanisms that aim to return the core temperature to the set point. One of the homeostatic mechanisms is shivering to generate heat.
Heat and, consequently, the core temperature increases. This occurs during hot summer days. The brain’s thermoregulatory control center responds, for example, by stimulating the eccrine sweat glands to secrete sweat to cool the body (via evaporative cooling).
Warm Up Name As Many Human Body Systems As You Can Remember. List The Organs Involved. Define Homeostasis. Provide An Example.
. The body maintains an optimal core temperature by internal physiological regulation through a body system composed of thermoreceptors in the hypothalamus, brain, spinal cord, internal organs, and great veins.
For example, when it’s hot, they tend to look for cool, shady places and/or don’t move much. During the cold season they seek warm places and tend to increase their activity. Some species, such as birds, huddle or huddle together for warmth.
Humans, in turn, devised certain tools, systems and equipment to help achieve a tolerable or ideal ambient temperature within their shelters.

For example, radiant heating in the form of steam radiators, radiant floor heating, in-wall heating, masonry heaters and passive solar heating can heat surfaces and objects efficiently and produce uniform and comfortable. Read more facts about radiant heating.
Examples Of Negative Feedback Loops
When the blood glucose level is low, the alpha cells of the pancreas secrete glucagon which stimulates the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose through glycogenolysis or producing glucose.
Examples of homeostasis in plants, homeostasis in the human body, maintaining homeostasis in the human body, what are some examples of homeostasis in the human body, human homeostasis examples, examples of homeostasis in biology, examples of how the body maintains homeostasis, homeostasis examples in the body, importance of homeostasis in the human body, articles on homeostasis in the human body, concept of homeostasis in the human body, examples of equilibrium in the human body