- Enzymes In Dna Replication And Their Function
- Dna Replication In Eukaryotes
- Match Enzymes To Their Role In The Dna Replication Process
- Single Molecule View Of Coordination In A Multi Functional Dna Polymerase
- Eukaryotic Dna Polymerases Are Multi Subunit Enzymes.
- Solved Question 1 Match The Following Enzymes To Their
- Self Replication Of Dna By Its Encoded Proteins In Liposome Based Synthetic Cells
Enzymes In Dna Replication And Their Function – DNA replication is necessary for the growth or replication of an organism. You started as a single cell and now consist of about 37 trillion cells! Each of these cells contains the same copy of DNA that originated from the first cell that was you. How did you get 37 million sets from one set of DNA, one for each cell? through DNA replication.
Knowledge of the structure of DNA helped scientists understand the process of DNA replication and DNA replication. It occurs during the synthesis (S) phase of eukaryotic
Enzymes In Dna Replication And Their Function

. DNA must be copied after each new daughter cell to produce a complete set of chromosomes
Dna Replication In Eukaryotes
DNA replication is called “semi-conservative”. This means that when a strand of DNA is replicated, each of the two original strands acts as a template for a new complementary strand. When the replication process is complete, there are two identical sets of DNA, each containing one of the original strands of DNA and one newly synthesized strand.
Which facilitates the process. There are four main enzymes that facilitate DNA replication: helicase, primase, DNA polymerase, and ligase.
DNA replication begins when the enzyme helicase unwinds and unzips the DNA molecule. If you remember the structure of DNA, you will remember that it consists of two long nucleotides held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary nitrogenous bases. It forms a ladder-like structure with a spiral shape. To initiate DNA replication, the helicase must unwind the molecule and break the hydrogen bonds that hold the complementary nitrogenous bases together. This causes the two strands of DNA to separate.
Small molecules called single-stranded binding proteins (SSBs) attach to the loose strands of DNA, preventing the helicase from repairing broken hydrogen bonds.
Chapter 9: Dna Replication
Figure 5.4.2 Helicase unwinds and unzips the DNA molecule. SSB prevents the two strands from reattaching to each other.
Once the nitrogenous bases from the inside of the DNA molecule are exposed, the creation of a new, complementary strand can begin. DNA polymerase creates the new strand, but it needs some help finding the right place to start, so primase places a small piece of RNA primer (shown in green in Figure 5.4.3). Once this short piece of primer is in place, DNA polymerase binds to the DNA molecule and begins attaching the nucleotides in the correct order to match the sequence of nitrogenous bases on the template (original) strand.
Figure 5.4.3 DNA replication. DNA replication is a semi-orthodox process. Half of the parent DNA molecule is conserved in the two daughter DNA molecules.

Figure 5.4.4 The two strands of nucleotides that make up DNA run parallel to each other. Note that the phosphate group is in the “up” position on the left-hand strand and the phosphate group is in the “down” position on the right-hand strand.
Match Enzymes To Their Role In The Dna Replication Process
If we think about the DNA molecule, we remember that the two strands of DNA run parallel to each other. This means that in the sugar-phosphate backbone, the sugar is oriented “up” on one strand of the DNA, while the phosphate is in the “up” position on the other strand (see Figure 5.4.4). DNA polymerase is an enzyme that can only work in one direction on a DNA molecule. This means that one strand of DNA can be copied into a long string, as the DNA polymerase follows the helicase as it unzips the DNA molecule. This strand is called the “leading strand”. However, since the DNA polymerase replicates in the opposite direction of the helicase unzipping, the other strand can only replicate in small pieces. This strand is called the “lagging strand”. These small pieces of DNA on the lagging strand are called Okazaki fragments.
Look at Figure 5.4.5 and find the Okazaki fragments, the leading strand and the lagging strand.
Figure 5.4.5 DNA polymerase can synthesize new DNA in only one direction on the template strand. This results in one group of DNA being replicated in one long strand (the leading strand) and one in smaller pieces called Okazaki fragments (the lagging strand).
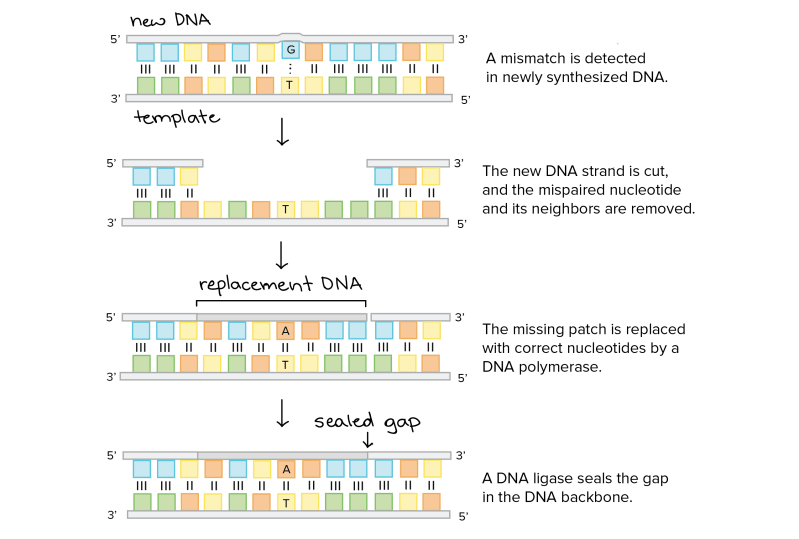
Once DNA polymerase has copied the DNA, a third enzyme called ligase completes the final step of DNA replication, repairing the sugar-phosphate backbone. It bridges the gaps in the spine between the Okazaki fragments. When this is done, the DNA returns to its classic double helix structure.
Solved Telomerases Perform Reverse Transcription And Are
When DNA replication is complete, there are two identical sets of double-stranded DNA, each with an original, template, DNA molecule and a strand newly synthesized during the DNA replication process. Because each new strand of DNA contains an old and a new strand, we describe DNA as semi-orthodox.
Helicase and single-stranded binding proteins (1) by Christine Miller is used under a CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/) license.
The Leading and Lagging Strand of Your Genome/ DNA Replication/ on Flickr is used under the CC BY-NC-SA 2.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/2.0/) license.

Betts, J. G., Young, K.A., Wise, J.A., Johnson, E., Poe, B., Crews, D.H., Korol, O., Johnson, J.E., and Womble, M. , Desaix, P. (2013, April 25) . Figure 3.24 DNA replication [digital image]. Inn
Single Molecule View Of Coordination In A Multi Functional Dna Polymerase
A cycle of growth and division that cells go through. It includes interphase (G1, S, G2) and mitotic phase.
The process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle.
Human Biology by Christine Miller is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License, unless otherwise noted. Protein Synthesis The genetic code – the sequence of nucleotides in DNA – is ultimately translated into the sequence of amino acids in proteins – the gene.
Traits such as eye color are determined by proteins built according to instructions laid down in DNA.
How Many Types Of Dna Polymerase Are Present In Bacteria?
How Genes Work Transcription The information contained in DNA is stored in blocks called genes Genes code for proteins Determine proteins.
Protein synthesis. DNA acts like an “instruction manual” – it provides all the information necessary for the actual act of translating the information.
Transcription and Translation Transcription uses DNA to make a single strand of RNA that is complementary to DNA base pairs. is the enzyme used.

Gene expression. Central dogma Information flows: DNA RNA protein Exclusion: Reverse transcriptase (retrovirus) RNA DNA RNA protein.
Eukaryotic Dna Polymerases Are Multi Subunit Enzymes.
Protein Synthesis Transcription and Translation. Translating the Genetic Code ■Genes: Coded DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within.
RNA, transcription, and the genetic code. RNA = Ribonucleic Acid – Nucleic acid Similar to DNA but with several differences in number of DNARNA strands21.
Chapter 10 “How Proteins Are Made”. Learning Objectives I will compare the structure of RNA to DNA. I will summarize the transcription process.
CH 12.3 RNA & Protein Synthesis. Genes are DNA instructions that control the production of proteins within a cell.
Solved Question 1 Match The Following Enzymes To Their
12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis Page 300. A. Introduction 1. Chromosomes are threadlike structures found in the nucleus of nucleic acids and proteins.
Write fast: Take your seat before the bell rings. Start your quick write-up: What is a gene? What is it coded for?
Transcription The part of the message encoded in a sequence of bases in DNA must be transcribed into a sequence of bases in RNA before translation.

Types of RNA Genetic information copied from DNA is transferred to 3 types of RNA: Messenger (mRNA) is a copy of the information in DNA, which is brought to the ribosome where it is translated into a protein. Ribosomal (rRNA) are like the protein factories of cells. Transfer (tRNA) is like bringing the amino acid to the ribosome. Blueprint Factory Truck
Self Replication Of Dna By Its Encoded Proteins In Liposome Based Synthetic Cells
Transcription The process by which a DNA sequence is copied to produce a complementary mRNA strand. In other words, genetic information is transferred from DNA to RNA. Like replication, but makes RNA. The beginning of the process that ultimately translates the genetic code (via mRNA) into a protein.
Key Points Transcription is the first step in gene expression. It involves copying the DNA sequence of a gene to make an RNA molecule. Transcription is carried out by enzymes called RNA polymerases, which link nucleotides together to form an RNA strand (using the DNA strand as a template). Transcription has three stages: initiation, elongation, and termination. In eukaryotes, RNA molecules must be processed after transcription: they are cleaved, 5′ capped, and put at their ends. Transcription is regulated separately for each gene in your genome.
Transcription and Translation Overview Basically, a gene is used to make a protein in a two-step process: Step 1: Transcription! Here, the DNA sequence of a gene is “rewritten” in RNA form. In eukaryotes like you and me, RNA is processed (often with a few bits snipped off) to make a final product called messenger RNA or mRNA. Step 2: Translation! At this stage, the mRNA is “decoded” to produce a protein (or part/subunit of a protein) containing a specific sequence of amino acids, a central theory of molecular biology called reverse transcription.
RNA polymerase
What Are The Steps Of Dna Replication?
Types of enzymes and their function, enzymes needed in dna replication, enzymes used in dna replication and their functions, enzymes involved in dna replication and their functions, enzymes and proteins in dna replication, dna replication and enzymes, enzymes used in dna replication, function of enzymes in dna replication, dna replication enzymes and their functions pdf, what are enzymes and what is their function, dna replication and enzymes involved, dna enzymes and their functions