Difference Between Curriculum Design And Curriculum Development – PRONTO’s curriculum packages are designed to meet local project needs and priority areas. To meet these needs, PRONTO International collaborates with in-country project leadership and local experts to determine project priority areas that inform the extracurricular package. Local experts know the unique needs of their settings well, and PRONTO International relies on this invaluable expertise.
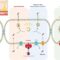
PRONTO’s curriculum development process encourages innovation, interaction, and iteration, and occurs in a three-tiered approach: planning, development, and implementation.
Difference Between Curriculum Design And Curriculum Development

Planning is an important part of the curriculum development process, laying the foundation for a successful program developed collaboratively with stakeholders. The planning phase includes:
Collaborative Curriculum Design For Sustainable Innovation And Teacher Learning
In the development phase, PRONTO International uses the information gathered in the planning phase to develop the appropriate curriculum.
During the implementation phase, PRONTO works with project partners to finalize all curriculum components and then trains implementers on how to use the curriculum to teach providers how to manage neonatal and maternal emergencies.
11000 + More than 11000 providers trained in 17 countries till 2022. 1300 + More than 1300 PRONTO Trainers and PRONTO Master Trainers trained in 17 countries. 14% improvement in mean self-efficacy score among participants after PRONTO training 62% increased goal achievement from strategic planning sessions at PRONTO-trained sites (8 months post-training intervention group) 21% decreased likelihood of cesarean delivery 12 months later” . . . Current Situations and Valuable Educational Ambitions There is always a need for newly developed curriculum models that address.—Edmund Short
Curriculum design refers to the structure or organization of the curriculum and includes the processes of curriculum development, curriculum planning, implementation, and evaluation. Curriculum models guide these processes.
Explore The Different Curriculum Design Models
Curriculum design is concerned with what should be included in the curriculum and how it should be presented so that the curriculum can be understood and implemented successfully (Barlow et al., 1984). Therefore, curriculum design refers to how the components of the curriculum are arranged to facilitate learning (Shiundu & Omulando, 1992).
Curriculum design is concerned with the issues of choosing what constitutes the structural framework or organizational basis of the curriculum. The choice of a design often indicates a value position.
As with other curriculum-related concepts, curriculum design has various definitions depending on the scholars involved. For example, Doll (1992) states that curriculum design is a method of organization that allows curriculum ideas to work. They also add that curriculum design refers to the structure or pattern of organization of the curriculum.

How a curriculum is conceived, organized, developed, and implemented depends on the educational goals of a particular state or district. Whichever outline is adopted depends on the philosophy of education.
Instructional Design Vs Curriculum Development In Elearning
There are many ways to design the school curriculum. These include subject-centered, learner-centered, integrated, or broad fields (combining two or more related subjects into one area of study; e.g., integrating the separate but related subjects of language arts, reading, writing, speaking, listening, and comprehension into a core curriculum).
This curriculum design refers to the organization of the curriculum on the basis of specific subjects, e.g. Geography, Mathematics, History etc. This is the oldest school curriculum design and the most common in the world. Even the ancient Greek teachers practiced it. Subject-centered design has been adopted by many European and African countries and states and districts in the United States. An examination of subject-based curriculum design shows that it is mainly used in upper elementary and secondary schools and colleges. Often, lay people, teachers and other professionals who support this design received their schooling or professional training in this type of system. For example, teachers are trained and specialize in teaching one or two subjects at the secondary and sometimes elementary school levels.
There are advantages and disadvantages to this approach to curriculum organization. There are reasons why some teachers advocate it while others criticize this approach.
It is possible and desirable to determine in advance what all children will learn in various subjects and grade levels. For example, curricula for schools in centralized education systems are generally developed and centrally approved by a governing body of the education body for a given district or state. In the US, state government often oversees this standards-driven process.
Curriculum Development: What Are The Various Types Of Core Curriculum Design?
Critics of subject-based curriculum design have strongly argued for a move away from it. These criticisms are based on the following arguments:
Considering the arguments for and against subject-based curriculum design, we can consider learner-centered or personalized curriculum design.
Learner-centered curriculum design may take various forms, such as individualized or personalized learning. In this design, the curriculum is organized around students’ needs, interests, abilities, and aspirations.

Proponents of design emphasize that attention is paid to what is known about human growth, development, and learning. This type of curriculum planning is done by working with the students after identifying their different concerns, interests and preferences and then developing appropriate topics according to the topics raised.
Curriculum Designer Cover Letter Example (free Guide)
This type of design requires a lot of resources and manpower to meet various needs. Therefore, the design is more used in the US and other Western countries, while use in developing countries is more limited.
In support of this approach, Hilda Taba (1962) stated, “Children prefer things that are related to the solving of real problems, that help them meet real needs, or that are related to active interests. Learning in the truest sense is an active transaction.
In broad fields/integrated curriculum design, two or three or more subjects are integrated into a broad course of study. This organization is a system of combining and reorganizing subjects related to the curriculum.
This approach seeks to develop some sort of synergy or unity into new areas for entire disciplines or even more branches of knowledge.
Our Curriculum Development Process
Proponents of broad fields/integrated designs believe that this approach brings integration and integration of knowledge. However, looking at the trend of events in curriculum practice in many states and countries, this may not be effectively realized. The main reason is that teachers are usually trained in two subjects at university level, so it is difficult for them to combine more areas than that. For example, general science may require physics, chemistry, biology, and geology, but science teachers only study two of these areas in depth.
The concept core curriculum is used to refer to the areas of learning within the school curriculum or any educational program required of all students. The core curriculum provides students with “general studies” or the general education required for all. Thus, the core curriculum is a section of the curriculum that teaches the concepts, skills, and attitudes that all individuals need to function effectively in society.
Separately taught subjects with little attempt to relate them to each other (e.g., mathematics, science, languages, and humanities may be taught as unrelated core subjects in high schools).

An integrated or “fused” core design is based on the overall integration of two or more subjects, for example:
Difference Of Curriculum Development And Instructional Design
There are a variety of curriculum design models to guide the process. Much of the design is based on the work of Ralph Tyler, who emphasized the role and place of goals in curriculum design.
Tyler’s model (1949) is based on the following four (4) basic questions he posed to guide the curriculum design process. They are as follows:
When applying Tyler’s model to curriculum design, the process begins with formulating curriculum objectives. Because of its emphasis on the importance of goals, it is considered an objective model. This process begins by analyzing information from various data sources. According to Tyler, curriculum data sources include:
From these sources, the designer develops general objectives. These undergo a screening process using philosophy of education and psychology of learning as key screens. Social values are also used as a screen, but sometimes these are incorporated into the philosophy of education. It serves several objectives that focus on education.
Solution: The Process Model Of Curriculum Design
Specific objectives are then derived from general objectives. For each specific objective, learning experiences are identified. In this context, learning experiences include subject/content and learning activities.
The next step is the organization of learning experiences. This is done to ensure that effective learning takes place. The various principles of organization include scope, order, integration, and continuity. The final step involves evaluation, determining the extent to which objectives have been achieved.
Feedback from the assessment is used to modify learning experiences and the entire curriculum as needed.

Learning experiences refer to the interaction between the learner and the external situations in the environment they encounter. Learning takes place through the active participation of students; It is not what the teacher does, but what the students learn.
Eclectic Model Of Curriculum Design
The problem of selecting learning experiences is the problem of determining which experiences are most likely to produce given educational goals.
Difference between curriculum and instruction, difference between curriculum and syllabus, difference between curriculum design and curriculum development, difference between web design and web development, difference between growth and development, difference between curriculum and curricula, difference between curriculum and program, difference between curriculum vitae and resume, difference between development and training, difference between learning and development, difference between instructional design and curriculum development, what is the difference between instructional design and curriculum development